Etching Wastewater Ammonia Removal Membrane System Project for an Optoelectronics Company
Release time:
2025-05-09
An optoelectronic technology limited company in the production process produces a large number of high ammonia nitrogen wastewater, in order to realize the wastewater discharge standards. The enterprise adopts advanced de-ammonia membrane technology to remove ammonia from the wastewater to ensure that the effluent quality meets the relevant environmental standards.
Etching Wastewater Ammonia Removal Membrane System Project for an Optoelectronics Companyphotoelectric technology limited company
1、Introduction
Water treatment refers to the natural waters or wastewater through a series of treatment processes to achieve a certain water quality requirements of the process. The commissioning of the water treatment system is to ensure that the normal operation of water treatment equipment and water quality to meet the key steps. In the commissioning process, we need to gradually adjust the parameters of the equipment to determine the best working conditions, and system monitoring and effect verification.
This paper describes the debugging process and results of the deammonia system. Through the debugging and optimization of the water treatment equipment, the normal operation of the water treatment system is ensured, and the treatment effect and water quality are improved. Through the monitoring and analysis of the system, the causes of the problems are identified and corresponding measures are taken to repair and improve the water treatment system to ensure the stability and reliability of the water treatment system.
2、Commissioning project
Name: A photoelectric technology limited company etching wastewater deammonia system project
Time: April 9, 2025-April 10, 2025
3、Commissioning objectives and tasks
The main goal of the water treatment site commissioning is to enable the deammonia equipment to meet the design indicators to ensure that the quality of treated water and water supply is stable and reliable. Specific tasks include:
1. debugging and checking of various equipment to ensure its normal operation;
2. collecting data on treated water and analyzing the data;
3. identifying problems and solving them;
4. writing commissioning reports to provide reference for subsequent operations.
4、Commissioning content试
4.1、Preparation before commissioning
1、Check the integrity of equipment and facilities;
2、Confirm whether the operation sequence and parameter setting of each equipment are correct;
3、Check whether the water quality of the water source meets the requirements (turbidity of raw water ≤ 2NTU, pH ≥ 12, etc.);
4, confirm the accuracy of the instrumentation.
5、Confirm whether the equipment is correctly installed and connected, sealed and fixed according to the design drawings.
6、Check whether the connection port of the equipment is fastened to prevent water leakage and other problems.
4.2、Commissioning process
According to the design requirements and water quality analysis results, adjust the parameters of the water treatment equipment, such as: influent flow, dosage, mixing time and so on. According to the actual situation for gradual adjustment, optimize the working conditions of the equipment to improve the treatment effect.
1, test the site manual valve in the correct position, prohibit the valve closed state start equipment;
2, start the raw water lifting pump, adjust the water intake 4-6 square meters per hour flow and control the raw water intake pH value is greater than 12;
3、Start the electric heater, heating the raw water to 40 degrees Celsius;
4, start the acid circulation pump, control the acid circulation flow at 10-20 square meters per hour and control the acid pH less than 1.5;
5, open the de-ammonia equipment, monitoring equipment operation and treatment of water quality changes. Through the collection and analysis of incoming and outgoing water samples, understand the changes in the water treatment process and determine whether the equipment is running normally. At the same time, real-time monitoring of equipment operating parameters, such as pH, flow, pressure, temperature, etc..
6、Sampling and recording relevant data.
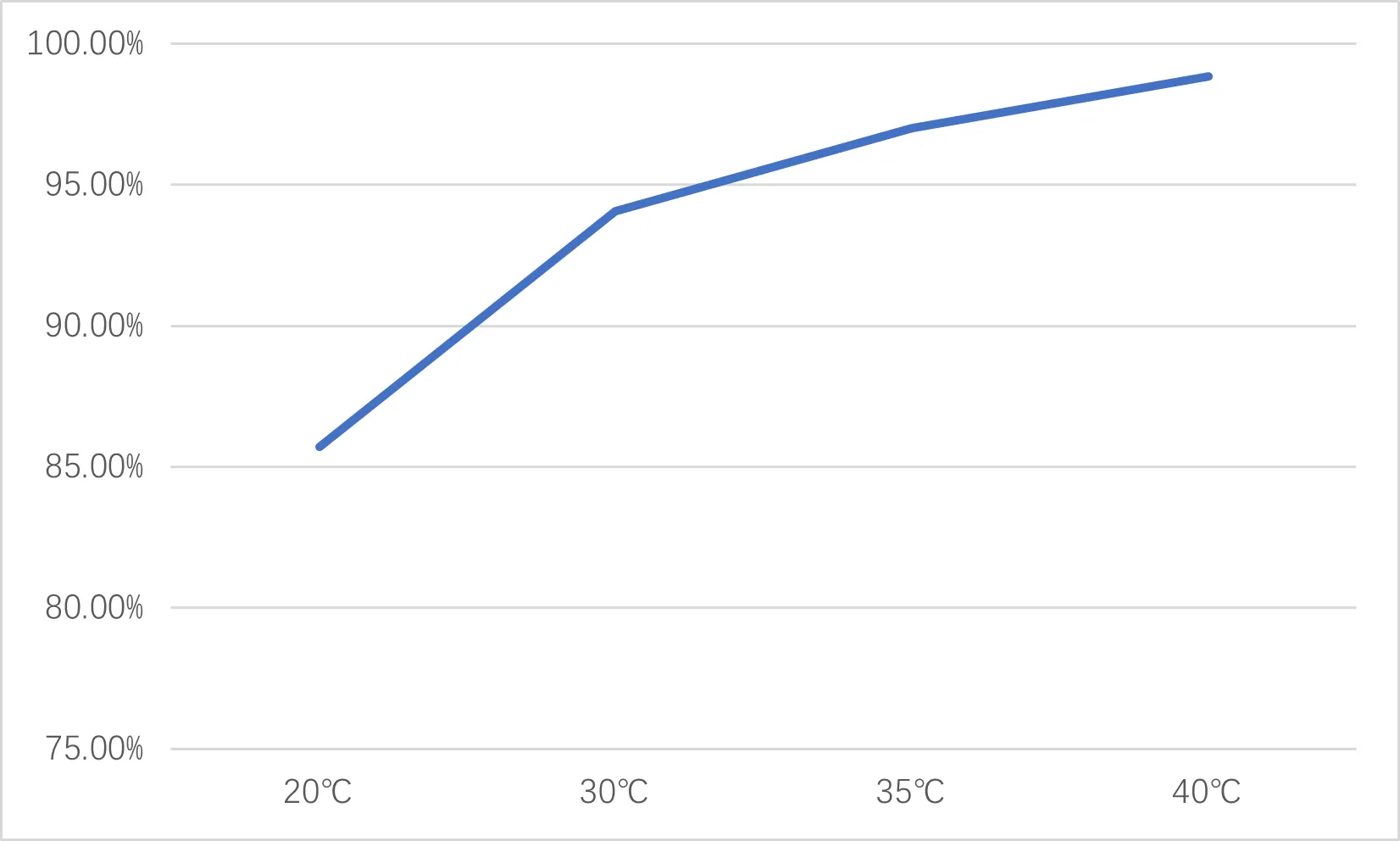
4.3、 Data logging
| Water Sample ID | Temperature | Ammonia Nitrogen | Removal Efficiency |
| Raw Water | / | 1680mg/L | |
| Treated Water | 20℃ | 240mg/L | 85.71% |
| Treated Water | 30℃ | 100mg/L | 94.05% |
| Treated Water | 35℃ | 50mg/L | 97.02% |
| Treated Water | 40℃ | 19.4mg/L | 98.85% |
Variations in Feedwater Pressure of PP-UF Filtration System (Table 2)
| Time | Pressure1(bar) | Pressure2(bar) | Remark |
| 2025-04-09 14:20 | 0.5 | 0.4 | Raw water sourced from new process line |
| 2025-04-09 14:40 | 0.6 | 0.48 | / |
| 2025-04-09 15:00 | 0.78 | 0.53 | / |
| 2025-04-09 15:20 | 1.2 | 0.75 | / |
The raw water from the new process line is introduced into the raw water tank without a sedimentation unit, resulting in excessive sediment accumulation and elevated influent turbidity.

5、Commissioning Summary
5.1、Analysis of Commissioning Results
Based on the collected data, analysis was conducted to identify operational issues. Identified anomalies were categorized, evaluated, and prioritized, followed by the development of corrective actions.
1、Data from Table 1 demonstrates that, under the condition of raw water pH ≥12, elevating water temperature to 40°C achieves >98% ammonia nitrogen removal efficiency, meeting design requirements.
2、Table 2 data indicates that inadequate raw water pretreatment (high suspended solids) caused PP-UF filtration system fouling, severely impacting continuous operation. Optimization of the sedimentation process is required to address this issue.
5.2、Debugging Recommendations
Post-Commissioning Recommendations & Corrective Actions
1、Add a sedimentation tank in pretreatment. Adjust raw water pH to 12–13 before it enters the sedimentation tank. Discontinue front-end dosing of fluoride removal agents and relocate dosing to downstream processes.
2、Replace the existing 10T acid circulation tank with a 3T tank. Add a dedicated 10T ammonium sulfate storage tank.
3、Modify the Level 3/4 ammonia removal membranes to operate in parallel with Level 1/2 membranes. Retain the original intermediate water pump. The intermediate tank can function as both the final treated water tank and the raw water tank for Levels 3/4 (if the effluent from Level 1/2 fails to meet discharge standards).
4、Revise field piping and instrumentation based on commissioning observations.
Latest News












